pleural effusion cat ultrasound
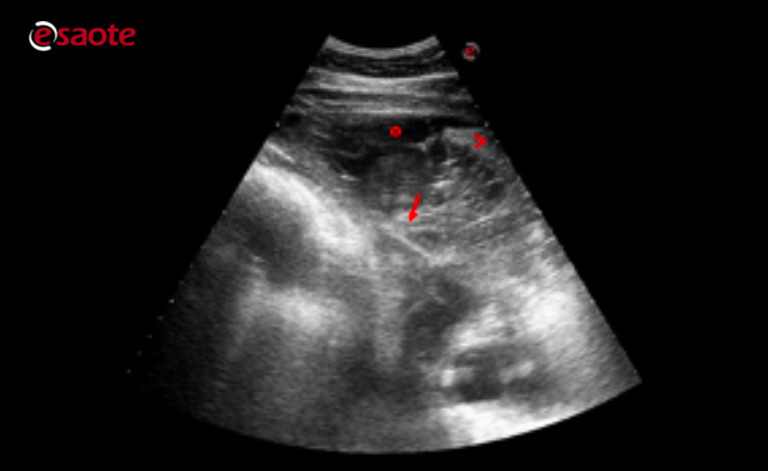
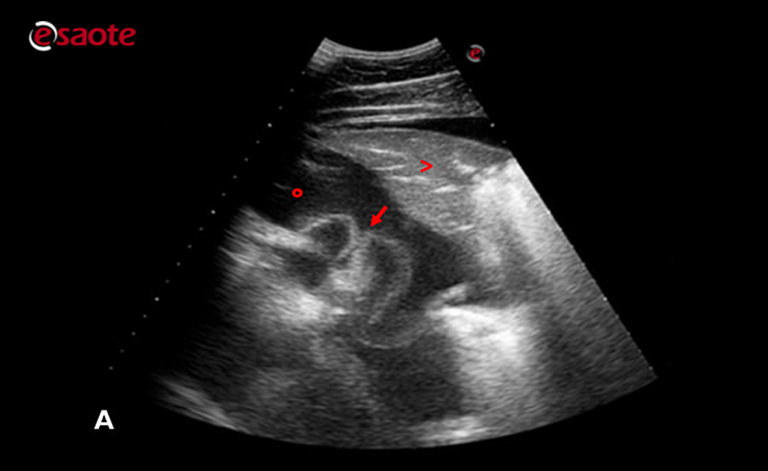
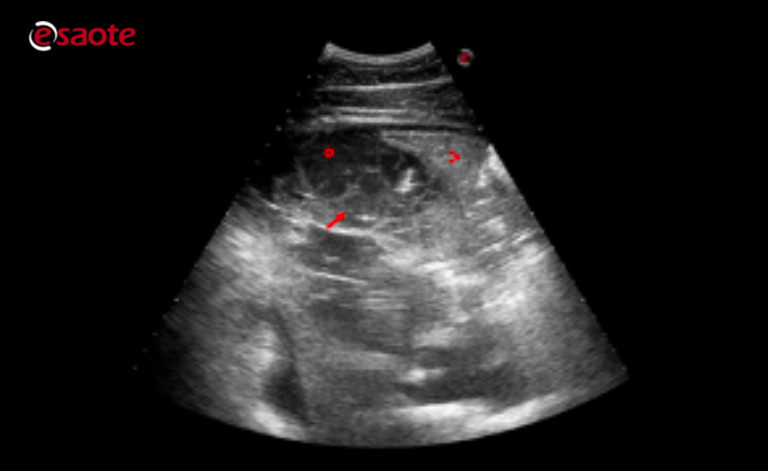
In pleural effusion the lungs are floating in a chest that is full of fluid. Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity.

Diagnostics Special Issue Lung Ultrasound A Leading Diagnostic Tool
Vet Radiol Ultrasound 1998.

. The type of pleural fluid withdrawn will enable your. Pleural effusion is commonly used as a catch-all term to describe any abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. There are a lot of causes of pleural effusion in cats transudate or exudate.
Thirty-two cats that received thoracic ultrasonography were found to have thoracic masses. Padrid P 2000 Canine and feline pleural disease. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing.
Presenting Signs of Pleural Effusion. 28 Saunders HM V anWinkle TJ Drobatz K. Testing that can help with diagnosis includes blood work urinalysis x-ray.
Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity. Etiology Prevalence and Epidemiology. Once fluid is identified in the chest cavity the cause must be determined.
In pleural effusion the fluid is not found within the lungs but instead within the pleural sac. This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the. The second most common cause of pericardial effusion in cats is cancer including tumors of the heart or pericardium.
The lack of specificity is mainly due to. Reichle J K Wisner E R 2000 Non-cardiac thoracic ultrasound in 75. Measurement of a pleural effusion volume with point-of-care ultrasonography may be a useful tool for intensivists and is an active area of research in critical care 7.
Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 30 6 1295-1307 PubMed. In the emergency treatment of pleural effusion cats are often first placed into an oxygen cage. How the fluid came to be in the pleural space is tied in with this.
Approach to pleural effusion in cats. Of the cats that received thoracic ultrasound most exhibited bilateral pleural effusion 93. Less commonly pericardial effusion in cats may be caused by an.
To a perinephric pseudocyst in a cat. Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space resulting from disruption of the homeostatic forces responsible for. A restrictive respiratory pattern with increased.
Unlike with a pericardial effusion in the case of accumulation of fluid in the pleural space there is no collapse of the heart walls. Cats with significant pleural space disease adopt a sternal position with abducted elbows. Regardless of your level of experience with ultrasound ruling out pleural and pericardial effusions is essential.
TFAST a standardized and validated thoracic point-of-care ultrasound examination includes 5 acoustic windows. A chest ultrasound to look for. A sample of pleural fluid obtained by piercing the cats chest cavity with a needle will be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the patient and. Cats presenting for pleural effusion are often experiencing shortness of breath. Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise.
This can be caused by thoracic lymphangiectasia swollen lymph vessels that leak chyle into the pleural. Of the 183 cats that received echocardiograms 21 had pericardial effusion with CHF as the primary cause of the pericardial effusion for 86 18 of these cats. Examination of the effusion included determination of specific gravity using a.
For those who are new to imaging around the heart with ultrasound differentiating. Bilaterally applied chest tube site and pericardial site views plus. The most commonly diagnosed cause of pleural effusion in cats is chylothorax.
Blood NTproBNP LUS and FCU evaluating left atrial LA size and presence of pericardial effusion PCEFF were performed in all cats. This fluid occupies space within the chest keeping the lungs from expanding as. Determining the underlying aetiology is key to appropriate management.
A thoracic chest ultrasound can also help. In the below clip from the Sonoscape S2. Collection of pleural effusion was performed by blind or ultrasound-guided thoracentesis.
Lung ultrasound findings including. In pleural effusion the fluid is not found within the lungs but instead within the pleural sac.
Lung Ultrasound Flooding In Fulminant Pulmonary Oedema In Cats And A Comparison With Pneumonia Vet Practice Support

Fig Ure 3 Abdominal Ultrasound Images Of A 9 Year Old Cat Case 4 With Download Scientific Diagram

A 10 Year Old Castrated Labrador Retriever Was Referred For Neurologic Evaluation After Presentation For Persistent Salivation The Dogs Intolerance Exercise

Cat Of Figure 1 Thoracic Ultrasound Revealed A Mild Hypoechoic Download Scientific Diagram

Selected Chest Ultrasound Images A Sea Shore Sign Granular Download Scientific Diagram

Pin By Sal Thompson On Radiography Medical Ultrasound Vision Eye Radiography

Vet Ultrasound Clinical Images
Animals Free Full Text Lung Ultrasound For Imaging Of B Lines In Dogs And Cats A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement Between Three Types Of Transducers And The Accuracy In Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema

Cardioechography Sonography Student Ultrasound School Ultrasound Physics

Pdf Thoracic Ultrasound A Method For The Work Up In Dogs And Cats With Acute Dyspnea Semantic Scholar

Utility Of Point Of Care Lung Ultrasound For Monitoring Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema In Dogs Murphy 2021 Journal Of Veterinary Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

Fast Tfast Ultrasound Examinations For Rapid Diagnosis In Emergency Patients Clinician S Brief

Different Types Of Pleural Effusion On Ultrasound Scan A Exudate B Download Scientific Diagram
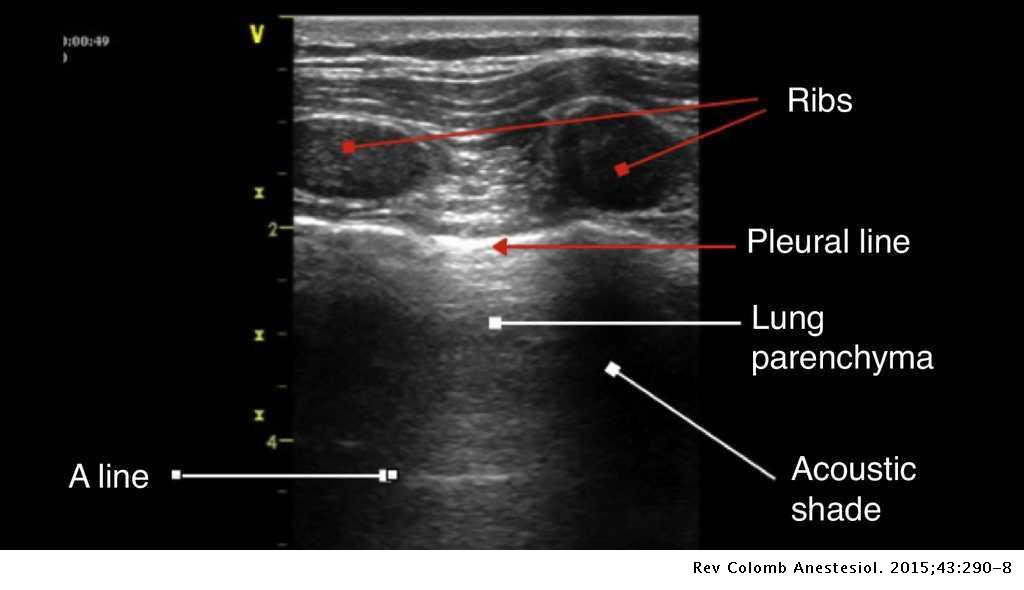
Semiology Of Lung Ultrasonography Dynamic Monitoring Available At The Patient S Bedside Colombian Journal Of Anesthesiology